| Chemical Engineering Program | Formal Name | Courses | Layouts | Max Capacity | Assignable Area (Sq. m.) | |
| Mechanics of Fluid Lab | Mechanics of Fluid Lab | Lab | 18 | 50 | ||
|
Entrance |
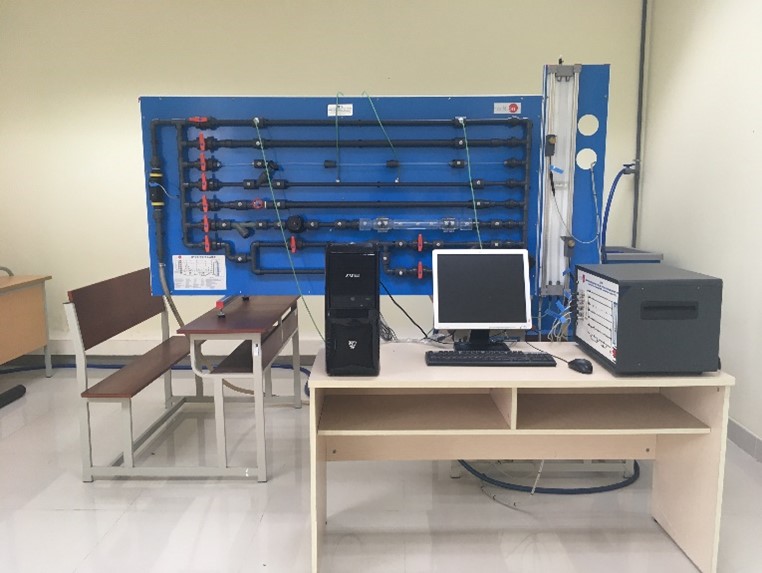
Computer controlled fluid friction in pipes unit |
|||||
|
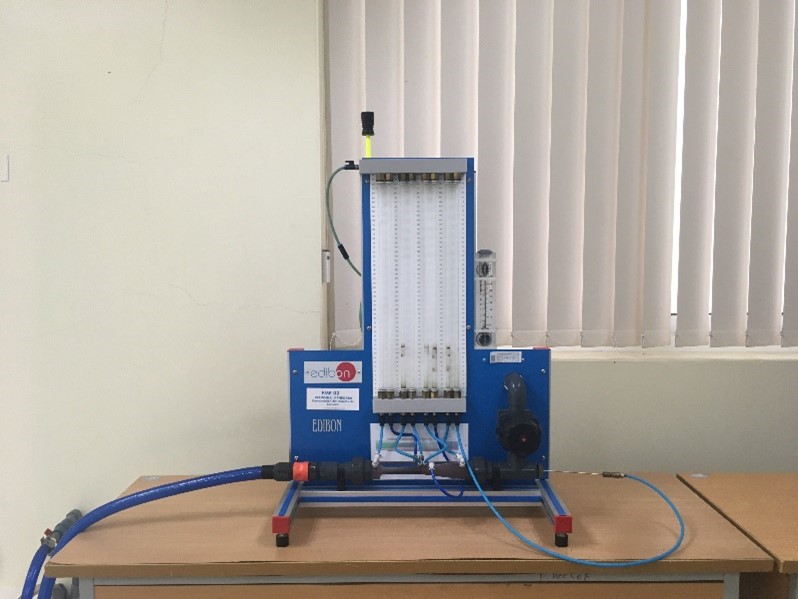
Bernoulli’s theorem demonstration unit |
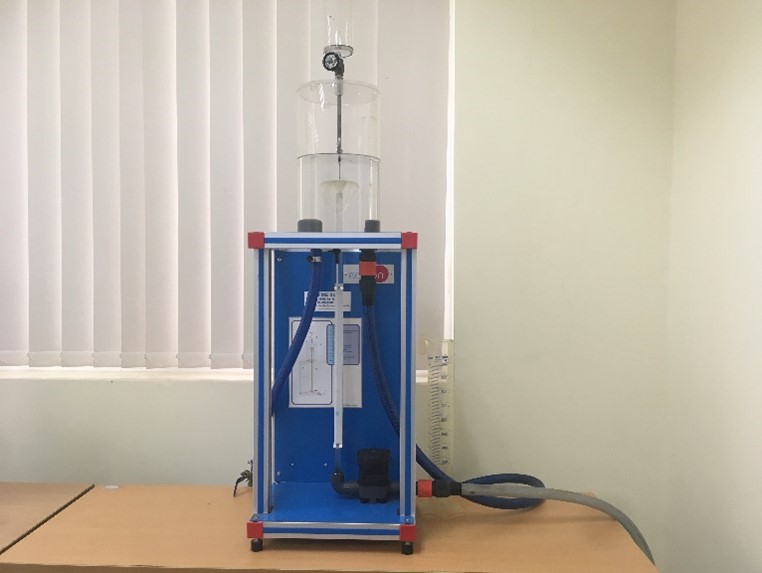
Osborne- Reynolds demonstration unit |
|||||
| Petroleum Engineering Program | Formal Name | Courses | Layouts | Max Capacity | Assignable Area (Sq. m.) | |
| Materials and Mechanical Lab | Strength of Materials | Lab | 8 | 60 | ||
|
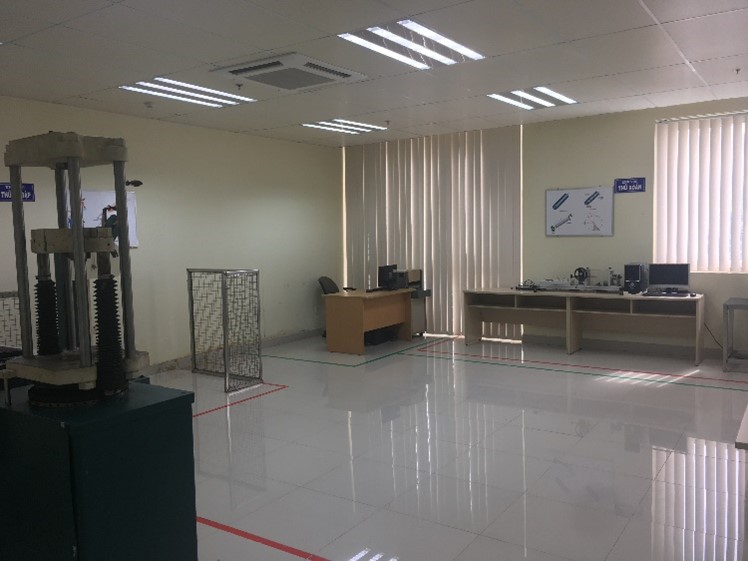
Entrance |
Lab layout |
|||||
|
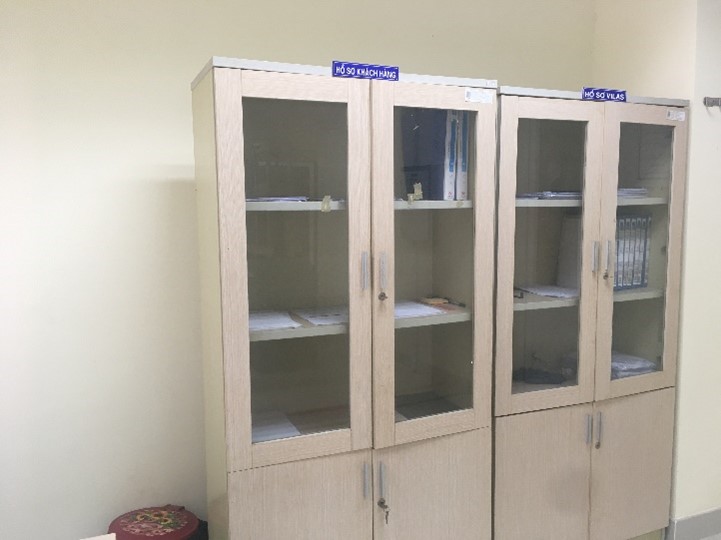
Document Cabinet |
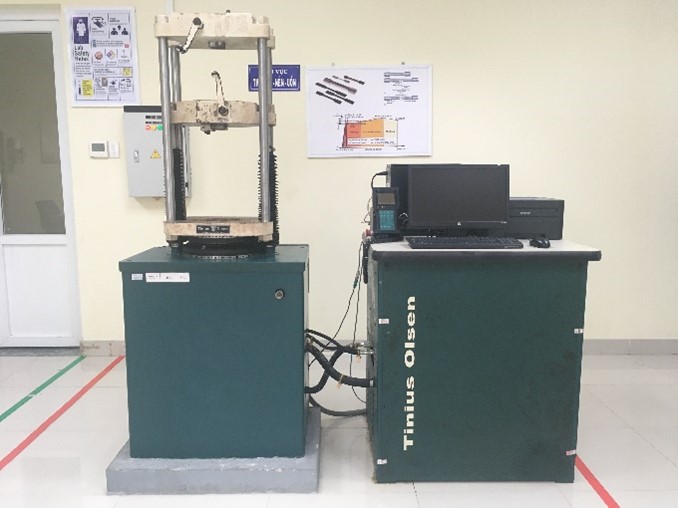
Tinius Olsen’s hydraulic Universal Testing Machine Model 300SL |
|||||
|
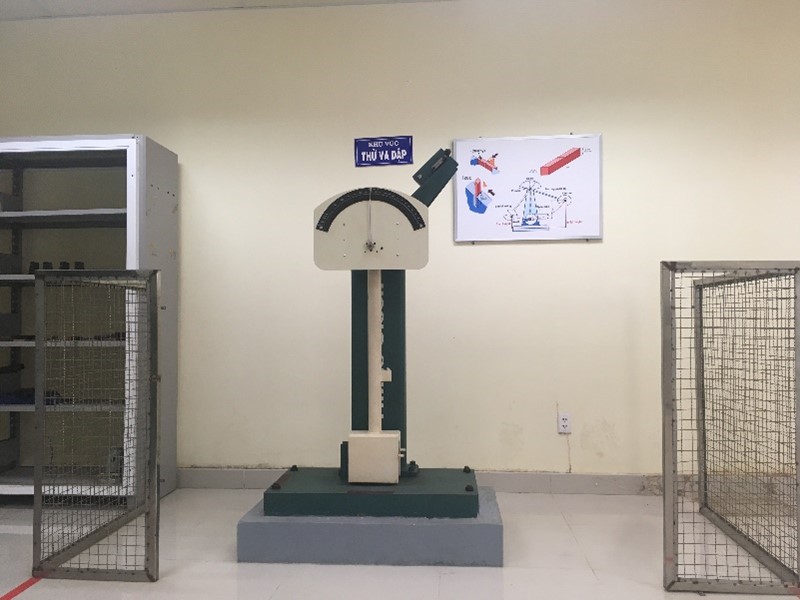
Tinius Olsen's pendulum impact tester |
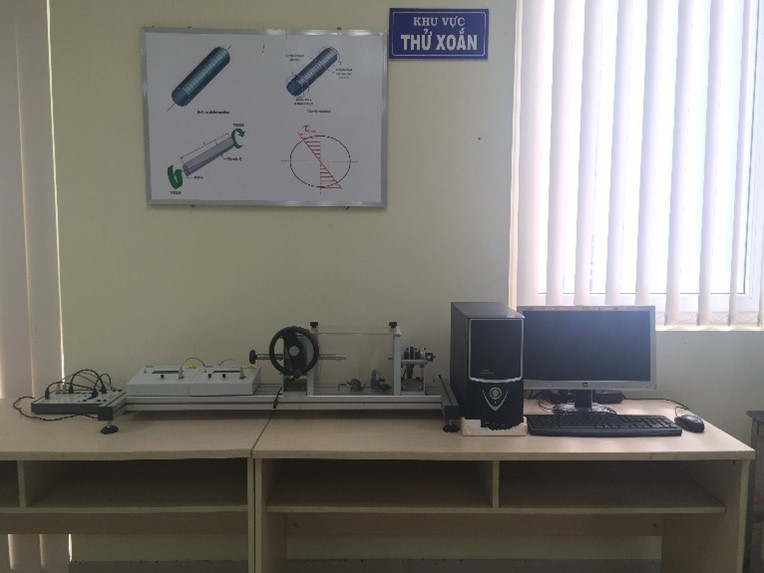
Torsion Testing Machine |
|||||
|
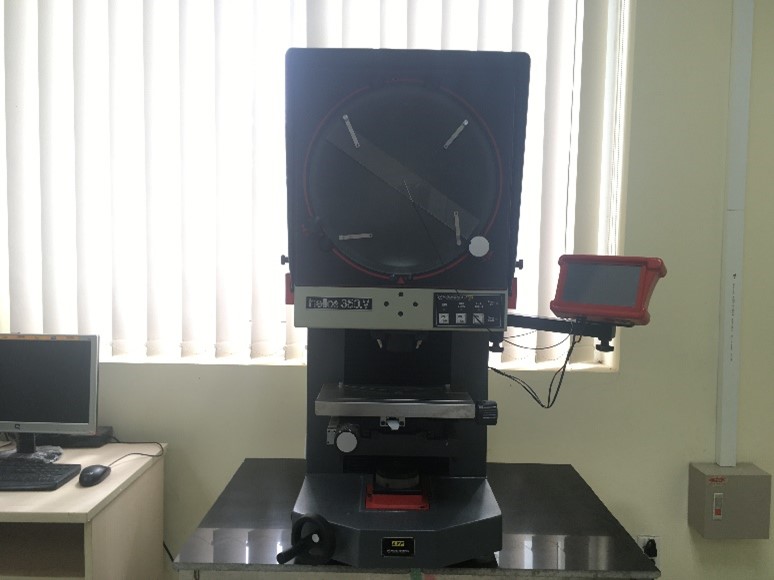
The Helios 350-V projector |
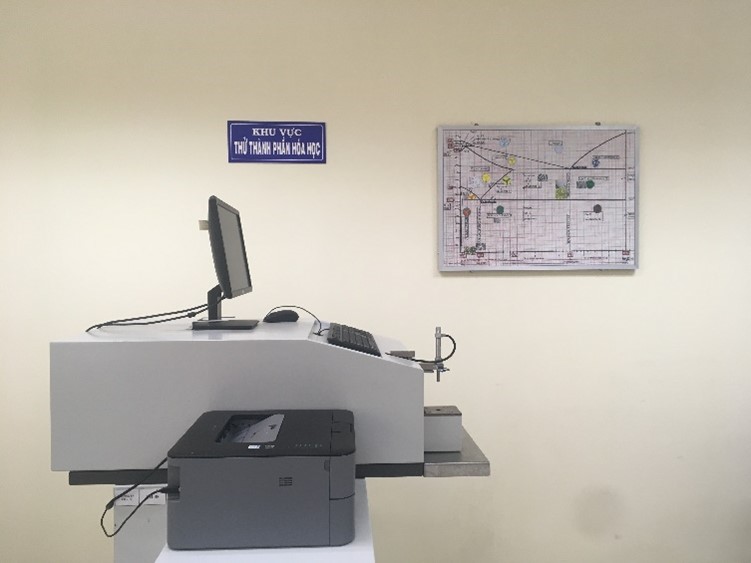
The OBLF Analyzer |
|||||
| Petroleum/Chemical Engineering Program | Formal Name | Courses | Layouts | Max Capacity | Assignable Area (Sq. m.) | |
| Electricity -Electronics Lab | Electricity -Electronics; Electrical Circuit Analysis | Lab | 24 | 60 | ||
|
Entrance |
Lab layout |
|||||
|
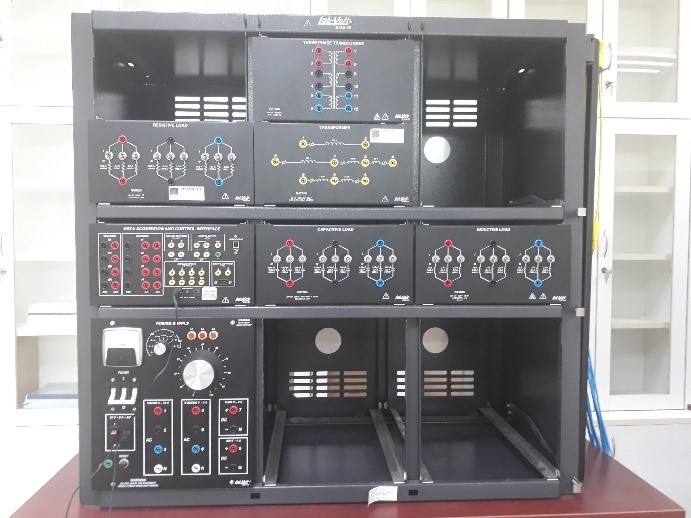
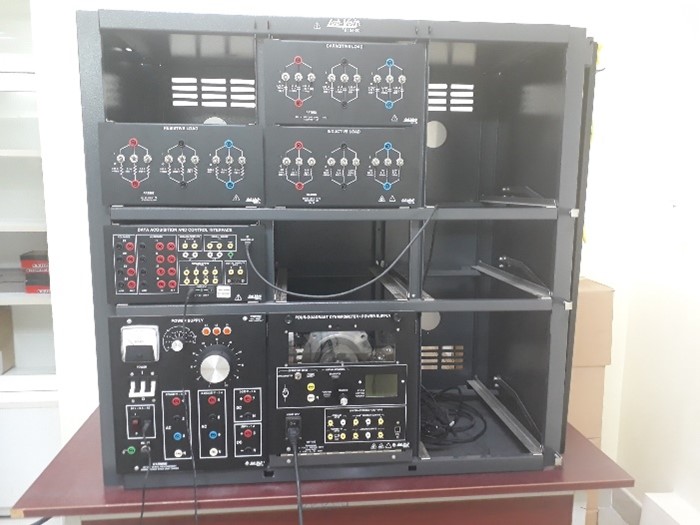
Power Supply, Data Acquisition Interface; Three phase circuit; 1-3 phase Transformers |
AC Motor/Generator, DC Motor/Generator, R-L-C Loads |
|||||
|
Power Supply, Three phase circuit; Data Acquisition Interface; R-L-C Loads |
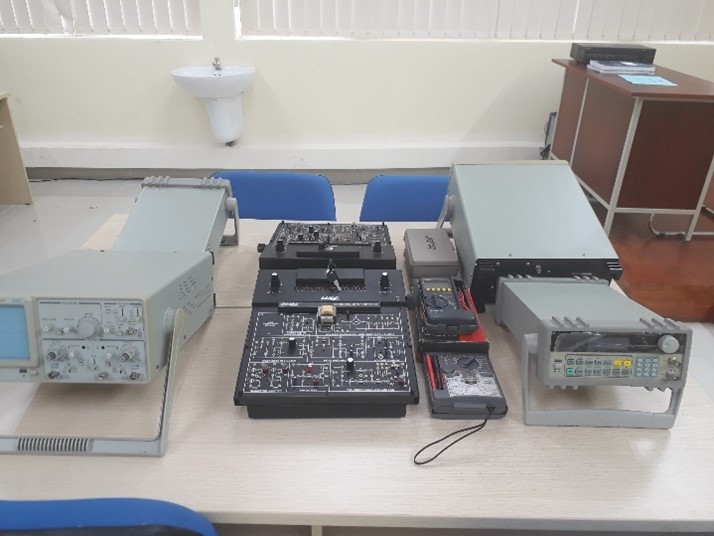
Electronic Devices, Osiloscop, Function Generators |
|||||
| PE/CE/GE Program | Formal Name | Courses | Layouts | Max Capacity | Assignable Area (Sq. m.) | |
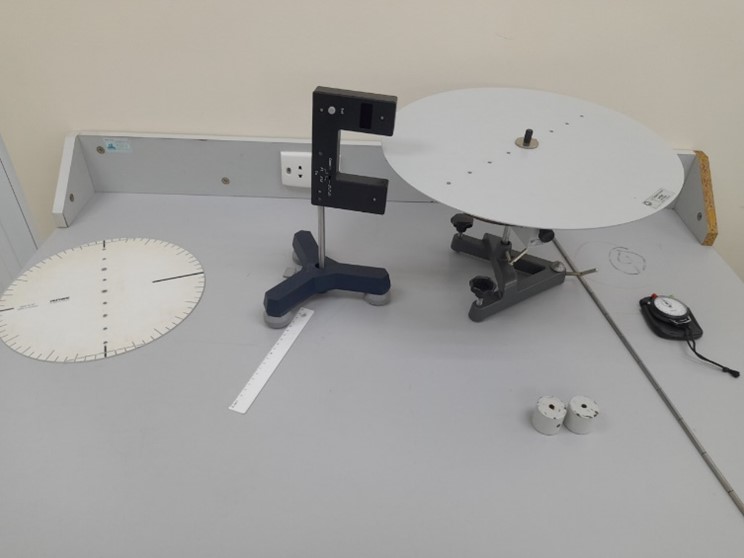
| General Physics Lab |
General Physics Lab 1 |
Lab | 40 | 140 | ||
|
Entrance |
Lab layout |
|||||
|
Measurement of length |
Measurement of volume and density |
|||||
|
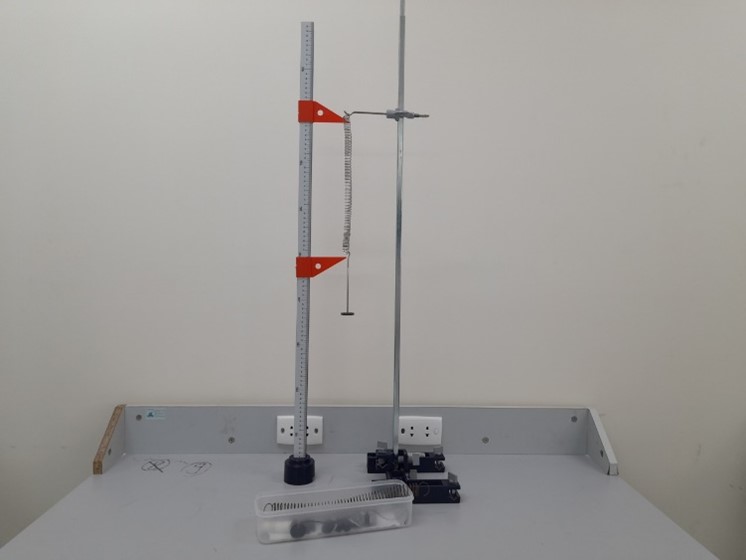
Inertia moment of rigid bodies |
Hooke’s law |
|||||
|
Simulated experiment of viscosity |
Simulated experiment of ideal gases |
|||||
|
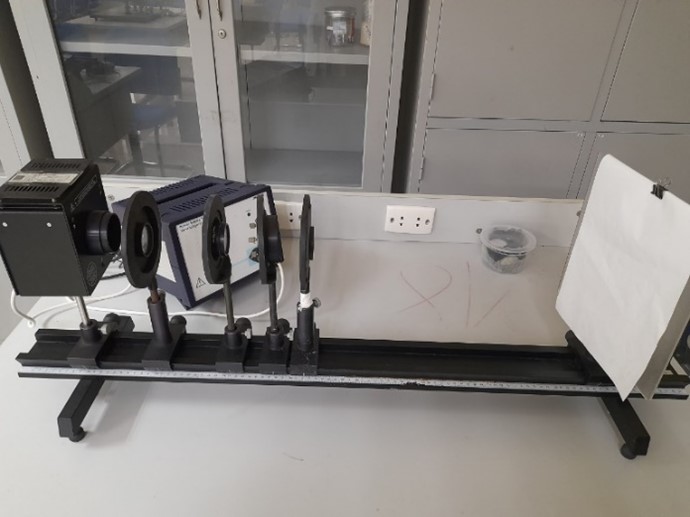
Simulated experiment of Bernoulli’s equation |
Transformer |
|||||
|
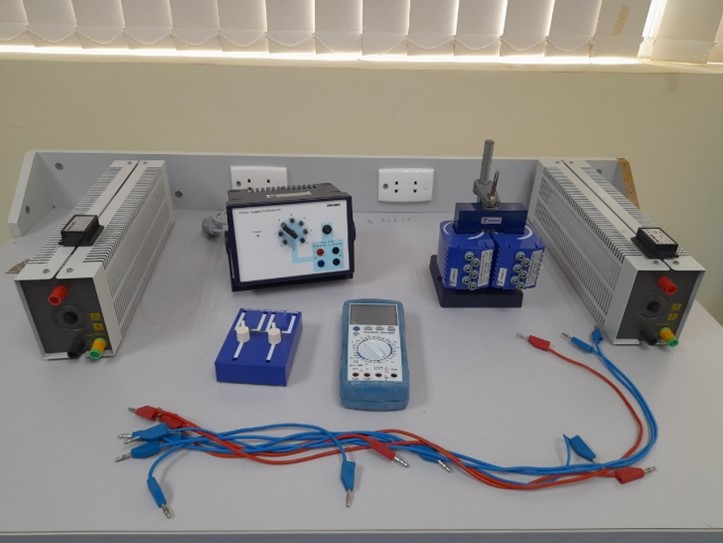
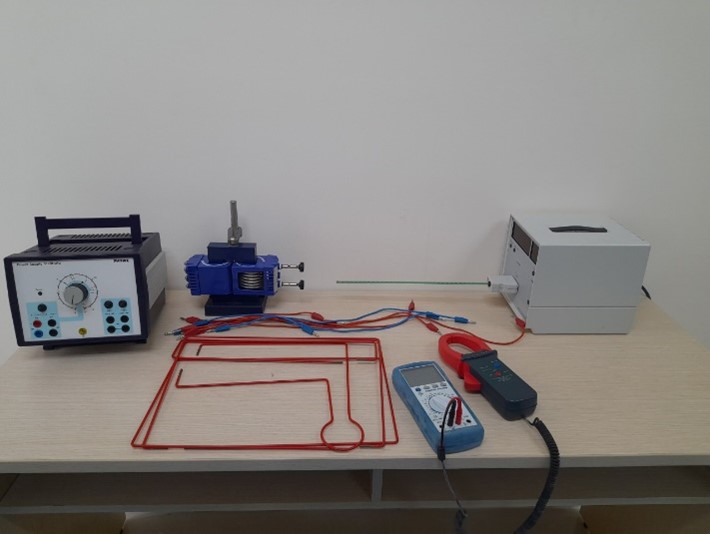
Magnetic field outside straight conductors |
Specific charge of the electron e/m |
|||||
|
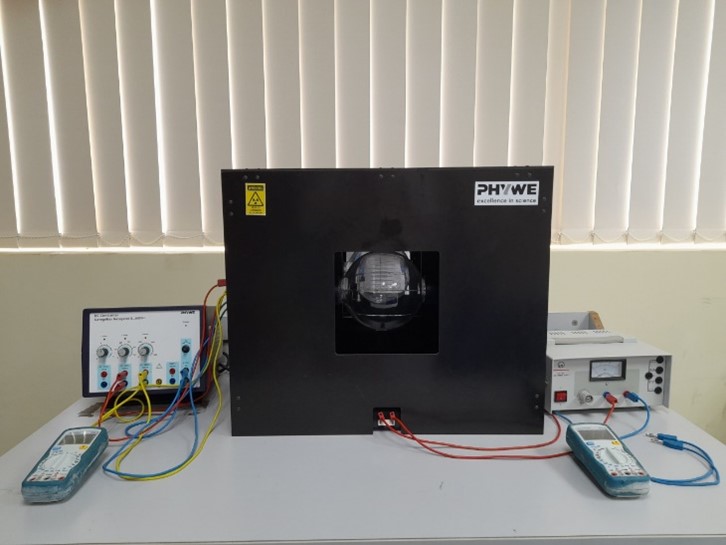
RLC measuring bridge |
Newton’s ring |
|||||
|
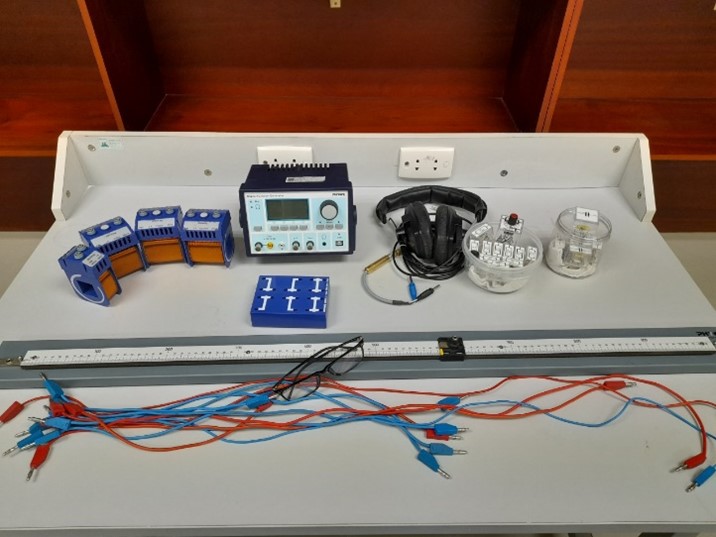
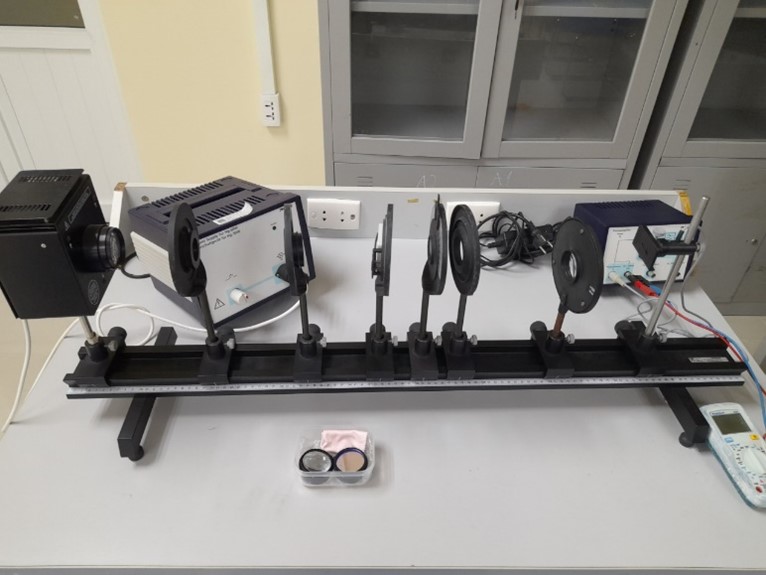
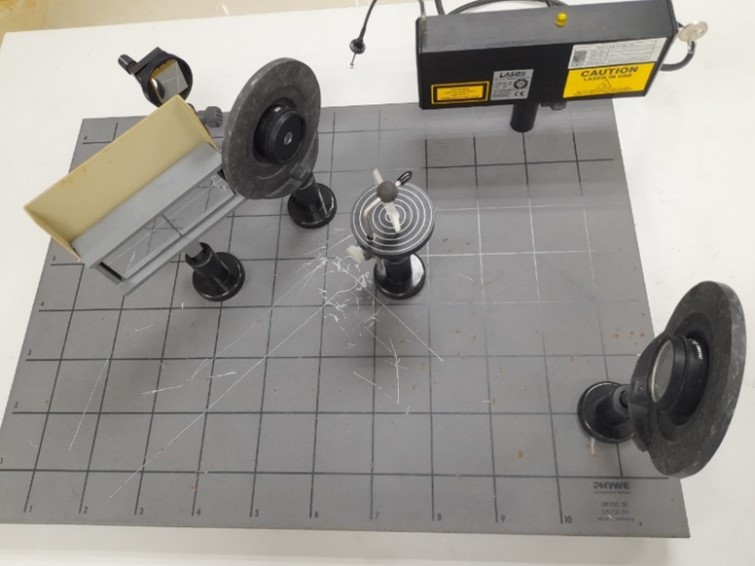
Interference by Fresnel’s mirror and biprism |
Polarization of light |
|||||
| Fundamental Chemistry Laboratory | |
| Instructor | Nguyen Van Kiet, Msc |
| List of experiments |
- Determination of molar mass using the ideal gas law - Determination of the enthalpy of combustion with a calorimetric bomb - Vapour pressure of mixtures of ideal fluids - Adsorption isotherms - Determining surface tension using the ring method (Du Nouy method) - Distribution equilibrium - Potentiometric titration - Kinetics of saccharose inversion - Conductivity of strong and weak electrolytes - The Nernst equation - Fractional distillation with the bubble tray column - Boiling point diagram of a binary mixture |
| Description about the lab |
General chemistry laboratory was established and have been operated by Faculty of Fundamental Sciences, PetroVietNam University (PVU). Right after the establishment PVU, the lab was built and invested two sets of experiments imported from PHYWE Group (Germany) with 2.5 billion VND fund. With modern equipment and facilities, the Fundamental Chemistry Laboratory basically meets the standard of a chemistry laboratory in accordance with the rules of Vietnam Ministry of Education and Training Vietnam. |
| Images of lectures |
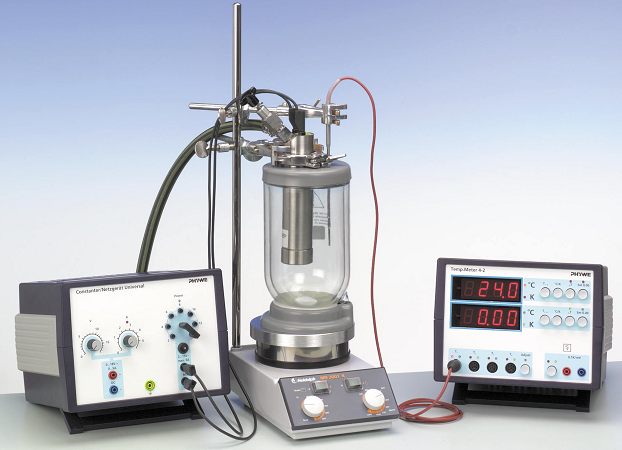
Lec_Kinetics of saccharose inversion
Lec_Vapour pressure of mixtures of ideal fluids
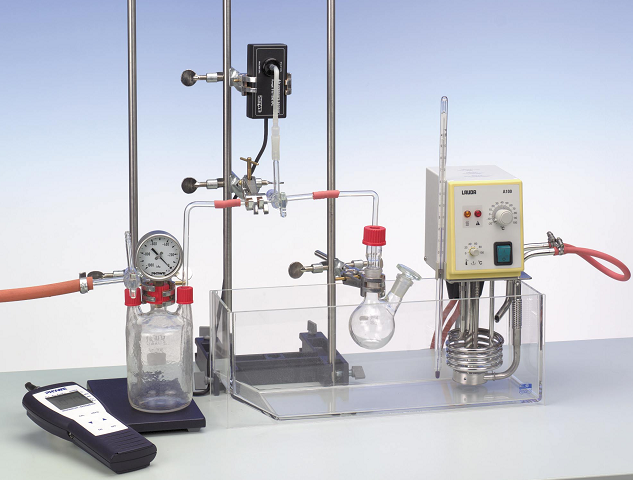
Lec_Determination of the enthalpy of combustion with a calorimetric bomb
Lec_ Fractional distillation with the bubble tray column |
| Chemical Engineering Program | Formal Name | Courses | Layouts | Max Capacity | Assignable Area (Sq. m.) | |
| General chemistry lab | General Chemistry Lab 1, 2 | Lab | 40 | 140 | ||
|
Entrance |
Lab layout |
|||||
|
Tools Cabinet |
Chemical Cabinet |
|||||
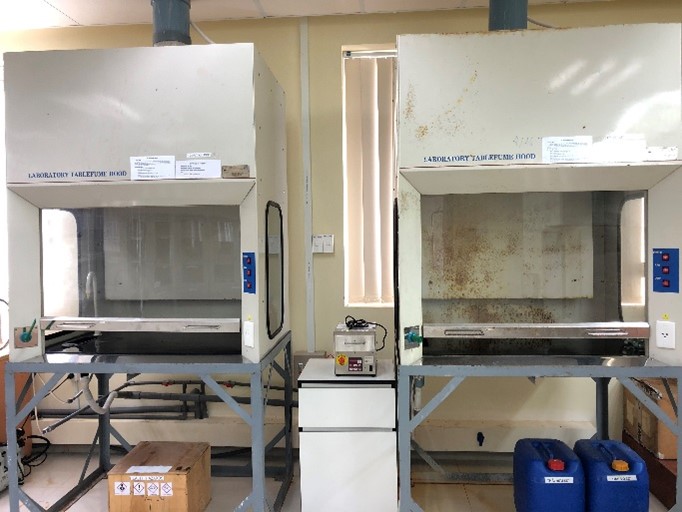
|
Fume hood |
Drying oven |
|||||
|
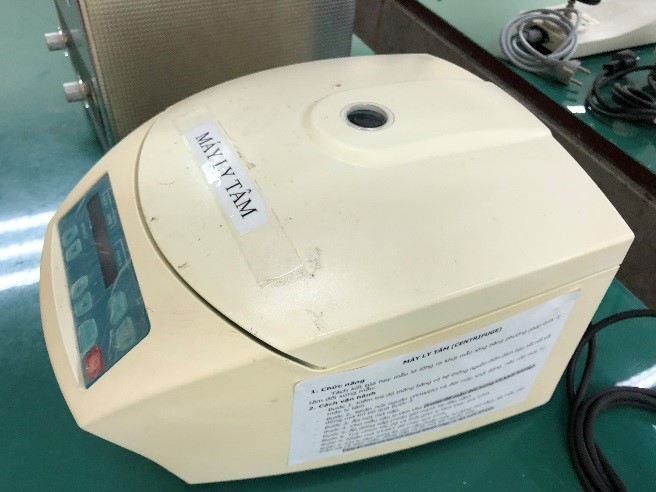
Ultrasonic cleaner |
Centrifuge |
|||||
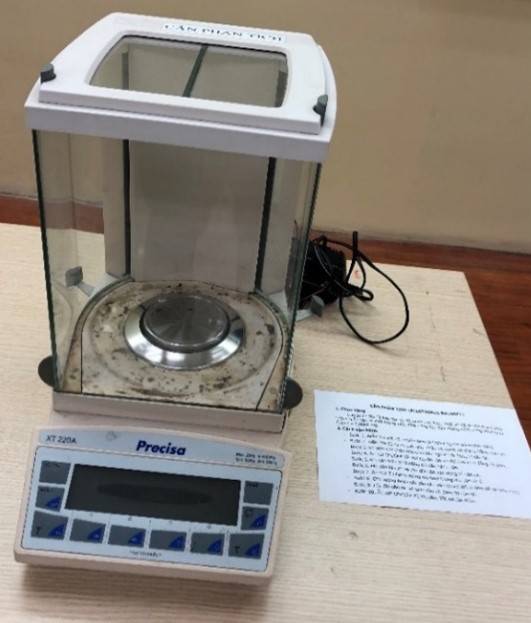
|
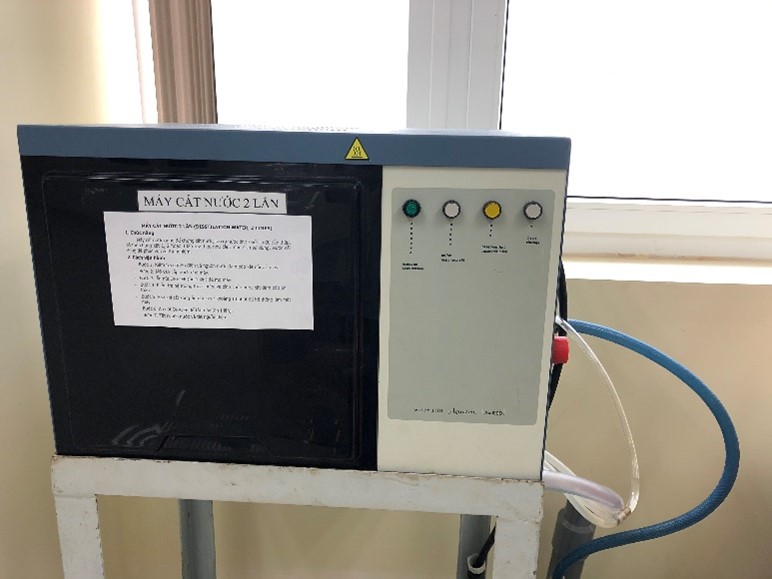
Analytical Balance |
Aquatron Water Still A4000D |
|||||
|
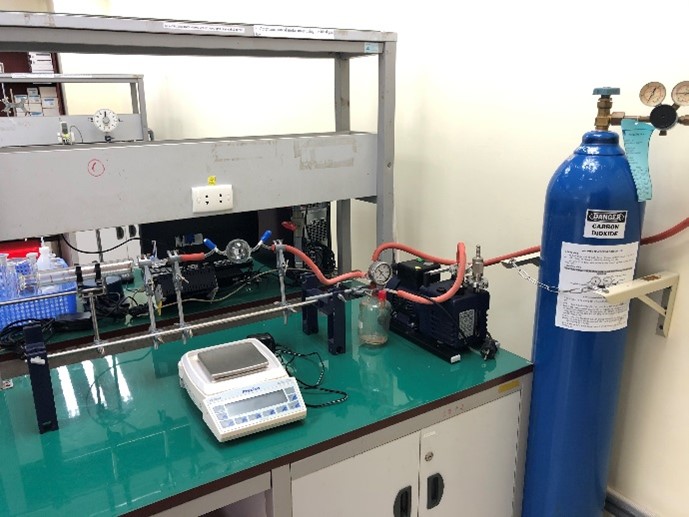
Lec 1. DETERMINATION OF MOLAR MASS USING THE IDEAL GAS LAW |
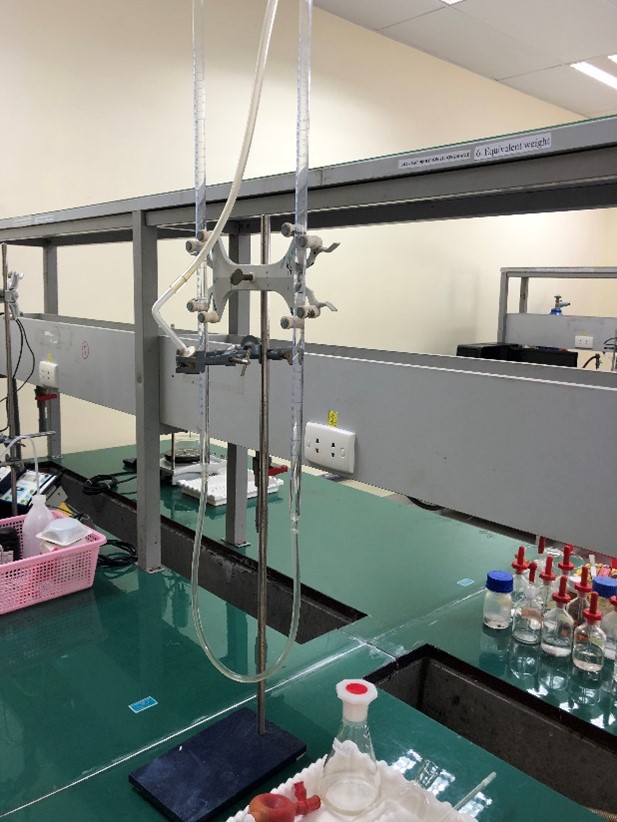
Lec 2. EQUIVALENT WEIGHT |
|||||
|
Lec 3. DETERMINATION OF STRONG AND WEAK ELECTROLYTES |
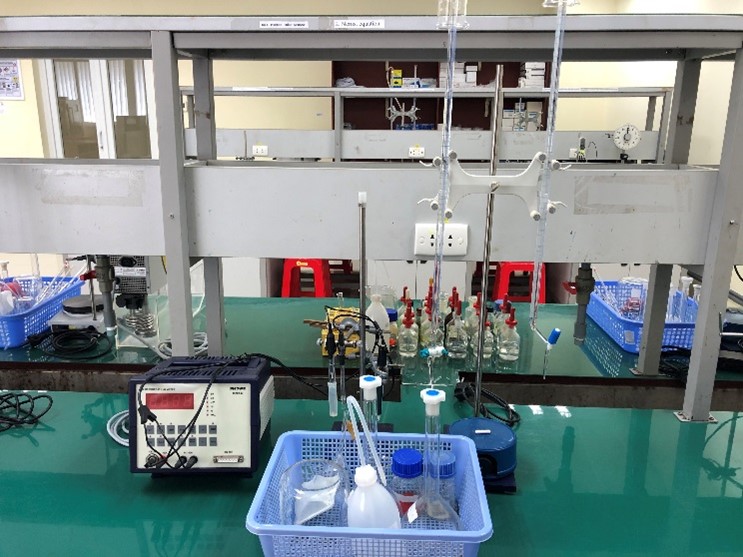
Lec 4. THE NERNST EQUATION |
|||||
|
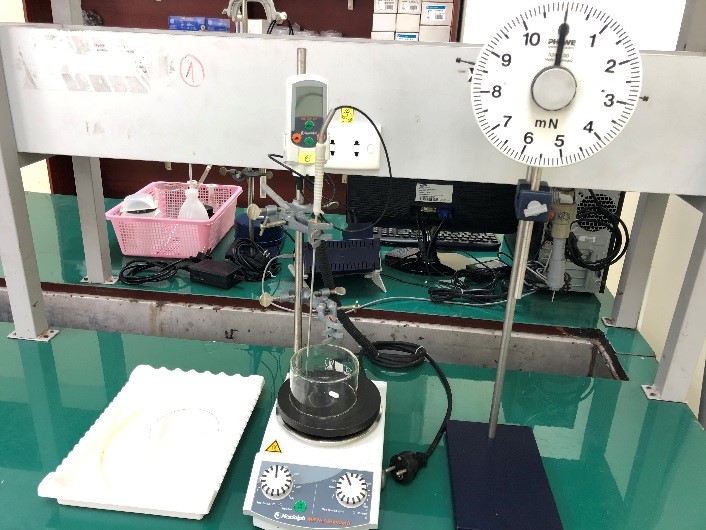
Lec 5. DETERMINING SURFACE TENSION USING THE RING METHOD |
Lec 6. POTENTIOMETRIC TITRATION |
|||||
|
Lec 7. KINETICS OF SACCHAROSE INVERSION |
Lec 8. REACTION RATE AND ACTIVATION ENERGY |
|||||